Elevated Command Prompt | Definition & How to Open
Jerry updated on Apr 17, 2023 to Knowledge Center | How-to Articles
Have you ever heard about the elevated Command Prompt? If you have not, you have come to the right spot. This article will describe what an elevated Command Prompt is and how to open an elevated Command Prompt.
Command Prompt is a practical utility in Windows computers. For example, you can clone a hard drive using the Command Prompt. However, when you try to conduct tasks with Command Prompt, it may require you to open an elevated Command Prompt with administrator-level privileges. This is because, by default, you do not have full rights, and not all commands operate when you open Command Prompt in Windows.
This post offered by EaseUS will describe the elevated Command Prompt and how to open an elevated Command Prompt in Windows.
If you open Command Prompt normally, you do not have full privileges to run some commands, and some commands will not work. To help shield Windows users from running commands that could harm their system or programs, this restricted mode was developed. This is because, by default, you will open cmd.exe without administrator-level permission.
An elevated Command Prompt or elevated command line allows a user to execute commands with administrative privileges. It is first introduced with Windows Vista to help users execute commands requiring administrative privileges.
Executing specific commands requires you to run an elevated Command Prompt. Or, you will encounter the Command Prompt not working issue. If you do not know if a command requires an elevated Command Prompt, it will tell you an error message after you run this command.
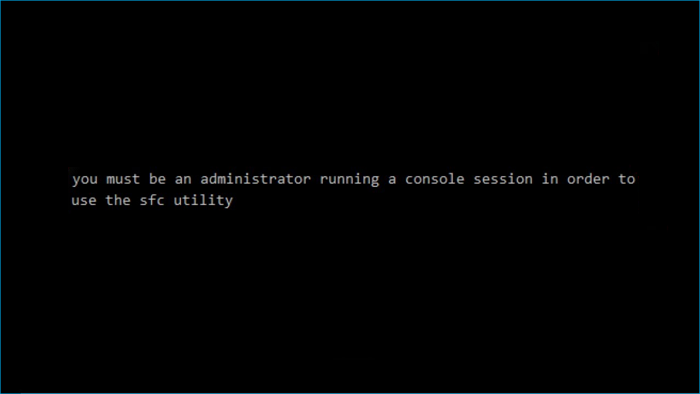
Typically, the message informs you that you should run a Command Prompt as an administrator to use the utility or execute a command. Therefore, you need to open an elevated Command Prompt to execute the command again.
You can apply one of the following methods to run an elevated Command Prompt easily and quickly in Windows 10.
Way 1. Run Elevated Command Prompt Using Run
Step 1. Press the Windows + R keys simultaneously, and type cmd in the Run box, then press the Ctrl + Shift + Enter keys.
Step 2. Click on Yes in the User Account Control window to run Command Prompt as administrator.
Way 2. Access Elevated Command Prompt from Start Menu
Step 1. Press the Windows key and type Command Prompt.
Step 2. Use the arrow keys to highlight the Command Prompt program from the search results on the left.
Step 3. Click Run as administrator on the right side of the window.
Way 3. Open Elevated Command Prompt from Task Manager
Step 1. Press the Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys to launch Task Manager in Windows 10. (Click More details to open Task Manger's advanced mode if needed.)
Step 2. Tap the File tab and select Run new task.
Step 3. In Create new task window, type cmd, and ensure the Create this task with administrative privileges box is checked. Then, click OK.
Step 4. Click on Yes in the User Account Control window to launch Command Prompt as administrator.
You can perform the steps below to open an elevated Command Prompt if your computer is running on Windows 7.
Step 1. Click the Start menu and locate Command Prompt under Accessories.
Step 2. Right-click on it and choose Run as administrator.
Step 3. Accept the pop-up User Account Control message to open an elevated Command Prompt.
A command prompt is an input field in one text-based user interface screen for an operating system or program with many usages. For example, you can back up files using the Command Prompt. This article has described the elevated Command Prompt and how to open elevated Command Prompt in different ways. Hopefully, you can find your answer in this article and find a way to use an elevated Command Prompt.
Related Articles
What Does Low Disk Space Mean on Windows 10/11/8/7, 2023 All Details You Want
Rollback from Windows 11 to Windows 10 - 2 Methods
Should I Get a NAS or External Hard Drive for Backup?
Website Builder Software | Web Design Software